Physical Quantity
Beside the fact that huge part of the subject Physics are about theories, it has also been defined that Physics is an experimental science. Experiments require measurements, and numbers are usually used represent this measurements. Physical quantities that needs to be considered are time, mass and length. Some example of measuring length or distance is by using a ruler and measuring time by using a stop watch. With this we can define the average speed of moving object as the distance traveled (measured by a ruler) divided by the time of travel (measured with a stop watch).
When we measure a quantity, we always compare it with some reference standard. This standard defines a unit of quantity. The meter is a unit of distance and second is a unit of time.
Here are some unit conversion factors.
 LENGTH:
LENGTH:
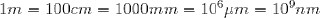
1km = 1000m = 0.6214mi
1m = 3.281ft = 39.37in
1cm = 0.3937in
1in = 2.540cm
1ft = 30.48cm
1yd = 91.44cm
1mi = 5280ft = 1.609km

1 nautical mile = 6080ft
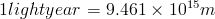
 TIME:
TIME:
1min = 60s
1h = 3600s
1d = 86,400s

Sample Problem:
Converting speed unit: The official world land speed record is 1228.0 km/h, set on October 15, 1997, by Andy Green in the jet engine car Thrust SSC. Express this speed in meters per second.
Solution:
Since we already know that
1km = 1000m and 1h = 3600s, then we can now directed solve the problem.
So we write,

where km/km = h/h = 1, the only unit left are m and s. Then we have,
 .
.
In my next post, I'll be writing on unit conversion for AREA.
When we measure a quantity, we always compare it with some reference standard. This standard defines a unit of quantity. The meter is a unit of distance and second is a unit of time.
Here are some unit conversion factors.
 LENGTH:
LENGTH: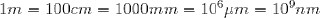
1km = 1000m = 0.6214mi
1m = 3.281ft = 39.37in
1cm = 0.3937in
1in = 2.540cm
1ft = 30.48cm
1yd = 91.44cm
1mi = 5280ft = 1.609km

1 nautical mile = 6080ft
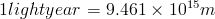
 TIME:
TIME:1min = 60s
1h = 3600s
1d = 86,400s

Sample Problem:
Converting speed unit: The official world land speed record is 1228.0 km/h, set on October 15, 1997, by Andy Green in the jet engine car Thrust SSC. Express this speed in meters per second.
Solution:
Since we already know that
1km = 1000m and 1h = 3600s, then we can now directed solve the problem.
So we write,

where km/km = h/h = 1, the only unit left are m and s. Then we have,
 .
.In my next post, I'll be writing on unit conversion for AREA.

Comments
Post a Comment